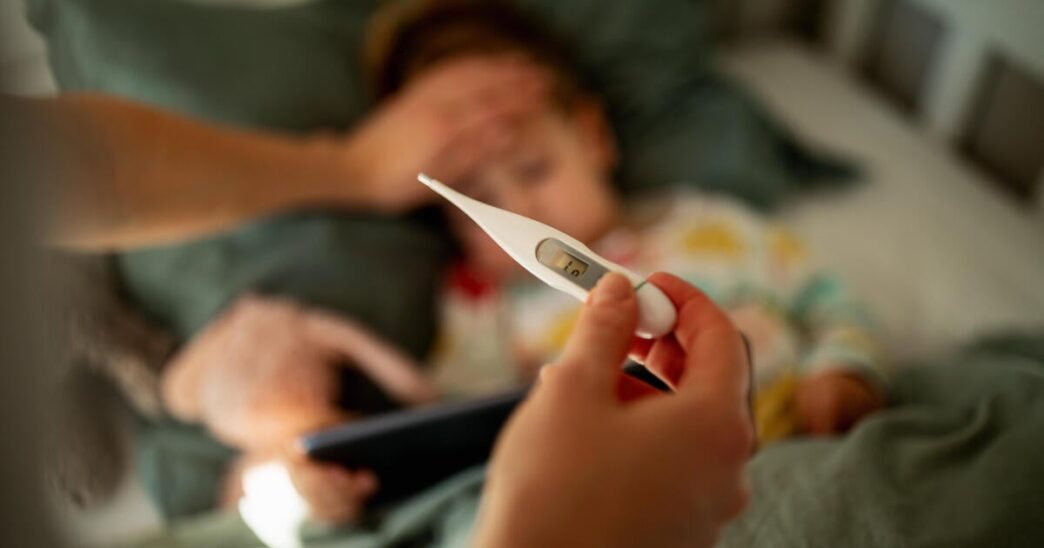
This season’s influenza vaccines may have been less effective against emergency room visits for some kids compared to last year, a new study by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggests, though effectiveness was still high against hospitalization.
So far this season, the vaccine’s protection against flu hospitalization was at least 63% for children and at least 41% for adults. These estimates of effectiveness against hospitalization, released Thursday in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, are considered high for flu vaccines.
But another metric of the shot’s effectiveness, looking at protection against infections that result in outpatient visits to places like urgent care clinics or emergency rooms, was worse. Effectiveness was 32% for children and adolescents, from the CDC’s U.S. Flu VE network of health care systems. That’s down from 67% in last year’s estimates.
Those figures are lower than from another network of outpatient providers in the report. The study’s authors suspect the decline is because of a difference in how many kids were infected in each by a strain of the flu virus called H3N2.
“The U.S. Flu VE network did not find statistically significant VE against influenza A(H3N2) in the outpatient setting among child and adolescent patients or among adult patients,” the study’s authors wrote.
Earlier data reported by the CDC suggested that this season’s flu vaccines might be poorly matched against many H3N2 strains this season. Around half of infections this past fall and winter were H3N2.
Scientists say that the protection offered by flu shots varies widely based on several drivers, not just how well-matched the shots are to what strains are circulating. A major factor is what kind of immunity people have from previous infections and vaccinations.
Estimates for effectiveness in adults from the same network was 36%. That is similar to the 33% at this time last year.
The new data comes as the U.S. is now seeing signs of a slowdown in influenza, after a record wave that reached some of the worst levels since the 2009 swine flu pandemic.